Implementation of CycleGAN for Gender Swapping on Pictures¶
In this notebook, I have implemented a Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Network - CycleGAN from scratch to swap genders of male and female pictures using the PyTorch framework. CycleGAN is an image-to-image translation model that basically maps the distribution of the input image to the output image by simultaneous training on pictures of these two domains. The advantage of this network is the capability of training over unpaired image datasets, which is usually the case in real-life.
Figure below from the original paper precisely summarizes how the model works introducing a cycle consistency loss in addition to the standard GAN loss.
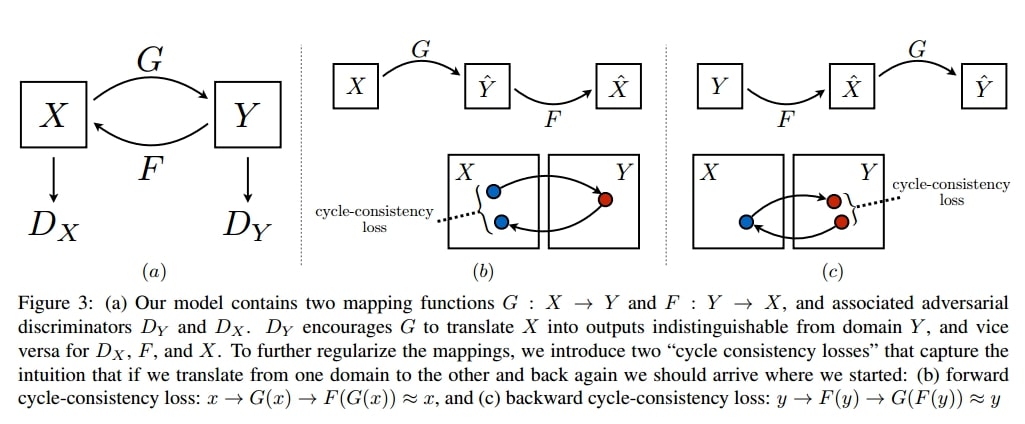
Furthermore, in order to maintain identity features of the images after translation, authors also propose to employ identity loss in the overall loss function. This new loss term helps preventing over-processing of an input image; meaning that it forces model to change only the relevant parts of the images, the faces in this case. Therefore the other general features of the image like color remains almost the same after a successful training.
Code¶
%matplotlib inline
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import itertools
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import os
from torch.utils import data
from collections import OrderedDict
from dataset_class import Dataset
from utils.img_pool import ImagePool
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datetime
#%config.InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = "7"
# CUDA for PyTorch
use_cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if use_cuda else "cpu")
Parameters¶
# Global parameters
epochs = 30
num_pairs = 200
num_residual_blocks = 6
Helper Functions¶
# Not used since implented as a module below.
def residual_block(inp, num_features):
"""
Transformation step of the generator.
inp: Input tensor to the residual block.
"""
in_ch = inp.shape[1] # Num of channels of the input tensor.
conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_ch, out_channels=num_features, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=1, padding=1)
conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=num_features, out_channels=num_features, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=1, padding=1)
return conv2(conv1(inp) + inp)
def conv_block(in_channel, out_channel, activation='relu', *args, **kwargs):
activations = nn.ModuleDict([
['lrelu', nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)],
['relu', nn.ReLU()]
])
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, *args, **kwargs),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel),
activations[activation]
)
def conv3x3(in_channels, out_channels, stride=1):
return nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
def get_image_pairs(data_dir, num_pairs=10, train_val_ratio=0.9):
# Determine the amount of pictures that will take place in train and validation sets
num_pairs_train = int(num_pairs * train_val_ratio)
# Read csv that comes with the celebA dataset.
d = pd.read_csv('{}/list_attr_celeba.csv'.format(data_dir))
# Get image_id and gender label (both type str) into numpy arrays for later masking.
males = np.array(d.nlargest(num_pairs, 'Male').get('image_id').values)
females = np.array(d.nsmallest(num_pairs, 'Male').get('image_id').values)
# Generate random index array.
idx = np.arange(num_pairs)
np.random.shuffle(idx)
# Create the random mask for both datasets.
train_mask = idx[:num_pairs_train]
val_mask = idx[num_pairs_train:]
# Get the masked male image_ids for train and val datasets.
train_male_ids = males[train_mask]
val_male_ids = males[val_mask]
# Get the masked female image_ids for train and val datasets.
train_female_ids = females[train_mask]
val_female_ids = females[val_mask]
# Return image_id lists as dictionaries.
tr_pairs = {'males': list(train_male_ids), 'females': list(train_female_ids)}
val_pairs = {'males': list(val_male_ids), 'females': list(val_female_ids)}
return tr_pairs, val_pairs
def print_images(im_list, save_dir, epoch_num, save_mode_on=True):
"""
Pytorch conv2d uses input & output dimensions as: (N, C, H, W).
To be able to plot the generated images, torch tensors must be converted back to (W,H,C)
and transferred back into the local memory by .cpu() function
"""
# A list that holds the necessary plot titles
titles = ['Real-A', 'Fake-B (A->B)', 'Recon-A (A->B->A)', 'Identity-A (A->A)',
'Real-B', 'Fake-A (B->A)', 'Recon-B (B->A->B)', 'Identity-B (B->B)']
# Plot output images in one master figure as subplots
im_idx = 0
fig, axarr = plt.subplots(2,4, figsize=(12, 6))
for i in range(2):
for j in range(4):
# Adjust network output image to proper dimensions.
im = im_list[im_idx].squeeze().T
# Scale from [-1..1] to [0..1] for plotting.
im = (im + 1) / 2.0
# Remove the numbers from the axes.
axarr[i, j].axis('off')
axarr[i, j].imshow(im.detach().cpu(), vmin=0, vmax=1)
axarr[i, j].set_title(titles[im_idx], fontweight="bold")
im_idx = im_idx + 1
#plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.0002) # Set spacing between subplots.
fig.tight_layout()
# Either save figures or just plot them
if save_mode_on:
plt.savefig(os.path.join(save_dir, 'epoch-{}.jpg'.format(epoch_num)))
plt.close()
else:
plt.show()
def assign_model_id(model_save_dir):
"""This method assigns a proper name to the model that will be saved.
"""
return 'ep_' + str(epochs) + '-pairs_' + str(num_pairs) + '-resblocks_' + str(num_residual_blocks)
Residual block¶
Implemented as a Pytorch module to gain ability of adding into a Sequential model.
# To-Do: Revise and decide relu and/or bnorm are needed or not.
# Residual block
class ResidualBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = conv3x3(in_channels, out_channels, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(out_channels, out_channels)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
Generator¶
Consists of 3 stages: encoding, transformation and decoding.
def create_generator():
model = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([]))
# Encoding
encoder = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('conv1', nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=(7,7), stride=1, bias=False, padding=3)),
('bnorm1', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)),
('relu1', nn.ReLU()),
('conv2', nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=2, bias=False, padding=1)),
('bnorm2', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)),
('relu2', nn.ReLU()),
('conv3', nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=2, bias=False, padding=1)),
('bnorm3', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)),
('relu3', nn.ReLU())
]))
model.add_module(name='encoder', module=encoder)
# Transformation
for i in range(num_residual_blocks):
model.add_module(name='res{}'.format(i+1), module=ResidualBlock(256,256))
# Decoding
decoder = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('deconv1', nn.ConvTranspose2d(256,64, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=2, padding=1, output_padding=1)),
('bnorm4', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)),
('relu4', nn.ReLU()),
('deconv2', nn.ConvTranspose2d(64,32, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=2, padding=1, output_padding=1)),
('bnorm5', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)),
('relu5', nn.ReLU()),
('reflectpad', nn.ReflectionPad2d(3)),
('conv4', nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=3, kernel_size=(7,7), stride=1, bias=True)),
('tanh', nn.Tanh())
]))
model.add_module(name='decoder', module=decoder)
return model
Discriminator¶
To help the generator to generate a high-resolution image, CycleGAN uses a technique called PatchGAN to created more fine-grained decision matrix instead of one decision value. Each value in this 32×32 decision matrix maps to a patch of the generated image, and indicate how real this patch is. In fact, we don’t crop a patch of the input image during implementation. We just need to use a final convolution layer to do the job for us. Essentially, the convolution layer performs like cropping a patch.
# In the original code lrelus are: LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
def create_discriminator():
# Last conv2d outputs a patch 30x30 as prediction matrix.
discriminator = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('conv', nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=(4,4), stride=2, padding=1)),
('lrelu1', nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)),
('convblock1', conv_block(in_channel=64, out_channel=128, activation='lrelu', kernel_size=(4,4), stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)),
('convblock2', conv_block(in_channel=128, out_channel=256, activation='lrelu', kernel_size=(4,4), stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)),
('convblock3', conv_block(in_channel=256, out_channel=512, activation='lrelu', kernel_size=(4,4), stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)),
('patch', nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=1, kernel_size=(4,4), stride=1, padding=1))
])) # Out shape: [1, 1, 30, 30]
return discriminator
Loss Functions¶
Cycle GAN has originally 3 loss functions as implemented below.
def gan_loss(pred, is_real):
# Typical GAN loss to set objectives for generator and discriminator
if is_real:
# Ex: torch.ones([2, 4], dtype=torch.float64, device=cuda0)
return F.mse_loss(pred, torch.ones(pred.shape).to(device))
else:
return F.mse_loss(pred, torch.zeros(pred.shape).to(device))
def cycle_loss(reconstructed_images, real_images):
# Cycle loss to make sure reconstructed image looks real
return F.l1_loss(reconstructed_images, real_images)
def identity_loss(identity_images, real_images):
# Identity loss to make sure generator won't do unnecessary change
# Ideally, feeding a real image to generator should generate itself
return F.l1_loss(identity_images, real_images)
GAN model¶
I have created a class to represent the cycyleGAN as a Pytorch nn.module. This will be useful to utilize nn.module functionality and overwrited steps such as forward and backward pass.
class cycleGAN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, learning_rate=2e-4):
nn.Module.__init__(self)
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
# Loss function coeffs
self.LAMBDA_CYCLE = 10.0
self.LAMBDA_ID = 0.5
# Image pool parameter
pool_size = 50
# Discriminate validation and train behaviour
self.is_training = True
self.save_losses = False
# Initialize the image pools for both domains.
self.fake_A_pool = ImagePool(pool_size)
self.fake_B_pool = ImagePool(pool_size)
# Create dictionaries to save the entire loss progress
self.tr_gen_loss_dict = {
'loss_gen_a2b': [],
'loss_gen_b2a': [],
'loss_id_a2b': [],
'loss_id_b2a': [],
'loss_cycle_a2b2a': [],
'loss_cycle_b2a2b': [],
'loss_gen_total': []
}
self.tr_dis_loss_dict = {
'loss_dis_b': [],
'loss_dis_a': [],
'loss_dis_total': []
}
self.val_gen_loss_dict = {
'loss_gen_a2b': [],
'loss_gen_b2a': [],
'loss_id_a2b': [],
'loss_id_b2a': [],
'loss_cycle_a2b2a': [],
'loss_cycle_b2a2b': [],
'loss_gen_total': []
}
self.val_dis_loss_dict = {
'loss_dis_b': [],
'loss_dis_a': [],
'loss_dis_total': []
}
# self.gen_loss_dict = {}
# self.dis_loss_dict = {}
self.im_list = []
self.generator_a2b = create_generator()
self.generator_b2a = create_generator()
self.discriminator_a = create_discriminator()
self.discriminator_b = create_discriminator()
# To-Do: Set optimizers' lr and betas parameters.
self.optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(self.generator_a2b.parameters(), self.generator_b2a.parameters()), lr=self.learning_rate)
self.optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(self.discriminator_a.parameters(), self.discriminator_b.parameters()), lr=self.learning_rate)
def forward(self, real_a, real_b):
# Cycle A -> B -> A
fake_a2b = self.generator_a2b(real_a)
recon_b2a = self.generator_b2a(fake_a2b)
# Cycle B -> A -> B
fake_b2a = self.generator_b2a(real_b)
recon_a2b = self.generator_a2b(fake_b2a)
# Use real B to generate B should be identical
identity_a2b = self.generator_a2b(real_b)
identity_b2a = self.generator_b2a(real_a)
# Save images in an ordered list to be printed at the end of each epoch.
self.im_list = [real_a, fake_a2b, recon_b2a, identity_b2a,
real_b, fake_b2a, recon_a2b, identity_a2b]
return fake_a2b, recon_b2a, fake_b2a, recon_a2b, identity_a2b, identity_b2a
def backward_G(self, real_a, real_b, fake_a2b, recon_b2a, fake_b2a, recon_a2b, identity_a2b, identity_b2a):
# To-Do: Move external loss funcs into the class.
if self.is_training:
# Ds require no gradients when optimizing Gs
self.set_requires_grad([self.discriminator_a, self.discriminator_b], False)
# Set G_A and G_B's gradients to zero
self.optimizer_G.zero_grad()
loss_identity_a2b = identity_loss(identity_a2b, real_b)
loss_identity_b2a = identity_loss(identity_b2a, real_a)
# Generator A2B tries to trick Discriminator B that the generated image is B
loss_gan_gen_a2b = gan_loss(self.discriminator_b(fake_a2b), True)
# Generator B2A tries to trick Discriminator A that the generated image is A
loss_gan_gen_b2a = gan_loss(self.discriminator_a(fake_b2a), True)
loss_cycle_a2b2a = cycle_loss(recon_b2a, real_a)
loss_cycle_b2a2b = cycle_loss(recon_a2b, real_b)
# Total generator loss
loss_gen_total = loss_gan_gen_a2b + loss_gan_gen_b2a \
+ (loss_cycle_a2b2a + loss_cycle_b2a2b) * self.LAMBDA_CYCLE \
+ (loss_identity_a2b + loss_identity_b2a) * self.LAMBDA_ID
if self.is_training:
# Calculate gradients
loss_gen_total.backward()#retain_graph=True)
# Update G_A and G_B's weights
self.optimizer_G.step()
if self.save_losses:
if self.is_training:
self.tr_gen_loss_dict['loss_gen_a2b'].append(loss_gan_gen_a2b.item())
self.tr_gen_loss_dict['loss_gen_b2a'].append(loss_gan_gen_b2a.item())
self.tr_gen_loss_dict['loss_id_a2b'].append(loss_identity_a2b.item())
self.tr_gen_loss_dict['loss_id_b2a'].append(loss_identity_b2a.item())
self.tr_gen_loss_dict['loss_cycle_a2b2a'].append(loss_cycle_a2b2a.item())
self.tr_gen_loss_dict['loss_cycle_b2a2b'].append(loss_cycle_b2a2b.item())
self.tr_gen_loss_dict['loss_gen_total'].append(loss_gen_total.item())
else:
self.val_gen_loss_dict['loss_gen_a2b'].append(loss_gan_gen_a2b.item())
self.val_gen_loss_dict['loss_gen_b2a'].append(loss_gan_gen_b2a.item())
self.val_gen_loss_dict['loss_id_a2b'].append(loss_identity_a2b.item())
self.val_gen_loss_dict['loss_id_b2a'].append(loss_identity_b2a.item())
self.val_gen_loss_dict['loss_cycle_a2b2a'].append(loss_cycle_a2b2a.item())
self.val_gen_loss_dict['loss_cycle_b2a2b'].append(loss_cycle_b2a2b.item())
self.val_gen_loss_dict['loss_gen_total'].append(loss_gen_total.item())
def backward_D(self, real_a, real_b, fake_a2b, fake_b2a):
# Re-assign fake_a2b and fake_b2a from the image pool.
fake_a2b = self.fake_B_pool.query(fake_a2b)
fake_b2a = self.fake_A_pool.query(fake_b2a)
if self.is_training:
self.set_requires_grad([self.discriminator_a, self.discriminator_b], True)
self.optimizer_D.zero_grad() # set D_A and D_B's gradients to zero
# Discriminator A should classify real_a as A
loss_gan_dis_a_real = gan_loss(self.discriminator_a(real_a), True)
# Discriminator A should classify generated fake_b2a as not A
loss_gan_dis_a_fake = gan_loss(self.discriminator_a(fake_b2a.detach()), False) # Detach added
# Discriminator B should classify real_b as B
loss_gan_dis_b_real = gan_loss(self.discriminator_b(real_b), True)
# Discriminator B should classify generated fake_a2b as not B
loss_gan_dis_b_fake = gan_loss(self.discriminator_b(fake_a2b.detach()), False) # Detach added
# Total discriminator loss
loss_dis_a = (loss_gan_dis_a_real + loss_gan_dis_a_fake) * 0.5
loss_dis_b = (loss_gan_dis_b_real + loss_gan_dis_b_fake) * 0.5
loss_dis_total = loss_dis_a + loss_dis_b
if self.is_training:
# Calculate gradients
loss_dis_total.backward()
# Update D_A and D_B's weights
self.optimizer_D.step()
# Save train and validation losses separately
if self.save_losses:
if self.is_training:
self.tr_dis_loss_dict['loss_dis_b'].append(loss_dis_b.item())
self.tr_dis_loss_dict['loss_dis_a'].append(loss_dis_a.item())
self.tr_dis_loss_dict['loss_dis_total'].append(loss_dis_total.item())
else:
self.val_dis_loss_dict['loss_dis_b'].append(loss_dis_b.item())
self.val_dis_loss_dict['loss_dis_a'].append(loss_dis_a.item())
self.val_dis_loss_dict['loss_dis_total'].append(loss_dis_total.item())
def set_requires_grad(self, nets, requires_grad=False):
"""Set requies_grad=False for all the networks to avoid unnecessary computations
Parameters:
nets (network list) -- a list of networks
requires_grad (bool) -- whether the networks require gradients or not
"""
if not isinstance(nets, list):
nets = [nets]
for net in nets:
if net is not None:
for param in net.parameters():
param.requires_grad = requires_grad
def optimize_parameters(self, real_a, real_b):
"""Calculate losses, gradients, and update network weights; called in every training iteration"""
# Forward
fake_a2b, recon_b2a, fake_b2a, recon_a2b, identity_a2b, identity_b2a = self.forward(real_a, real_b) # compute fake images and reconstruction images.
# G_A and G_B
self.backward_G(real_a, real_b, fake_a2b, recon_b2a, fake_b2a, recon_a2b, identity_a2b, identity_b2a) # calculate gradients for G_A and G_B
# D_A and D_B
self.backward_D(real_a, real_b, fake_a2b, fake_b2a) # To-Do: Query fake images from the pool.
Manage Directories¶
This method arranges and checks out all the necessary folder structure to save the output pictures, loss graphs and the model parameters. Utilizing date and time for unique naming.
def manage_folders():
currentDT = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y_%m_%d-%H:%M")
cur_dir = os.getcwd()
if not os.path.isdir(os.path.join(cur_dir, 'Output')):
os.mkdir(os.path.join(cur_dir, 'Output'))
output_folder = os.path.join(cur_dir, 'Output')
output_folder = os.path.join(output_folder, currentDT)
os.mkdir(output_folder)
graph_save_dir = os.path.join(output_folder, 'loss-graphs')
if not os.path.isdir(graph_save_dir):
os.mkdir(graph_save_dir)
im_save_dir = os.path.join(output_folder, 'generated-images')
if not os.path.isdir(im_save_dir):
os.mkdir(im_save_dir)
tr_im_save_dir = os.path.join(im_save_dir, 'train')
if not os.path.isdir(tr_im_save_dir):
os.mkdir(tr_im_save_dir)
val_im_save_dir = os.path.join(im_save_dir, 'val')
if not os.path.isdir(val_im_save_dir):
os.mkdir(val_im_save_dir)
model_save_dir = os.path.join(output_folder, 'saved-models')
if not os.path.isdir(model_save_dir):
os.mkdir(model_save_dir)
# Check if the directories exist
assert(os.path.isdir(im_save_dir)), 'Check your im_save_dir path.'
assert(os.path.isdir(graph_save_dir)), 'Check your graph_save_dir path.'
print('-----Directories to save the output-----\nTrain Fake Images: {}\nVal Fake Images: {}\nLosses: {}\nModel: {}'.format(tr_im_save_dir, val_im_save_dir, graph_save_dir, model_save_dir))
return tr_im_save_dir, val_im_save_dir, graph_save_dir, model_save_dir
Dataset¶
data_dir = '/celeba-dataset/'
# Make sure that the directory exists
assert(os.path.isdir(data_dir)), 'Check your data path.'
tr_pairs, val_pairs = get_image_pairs(data_dir, num_pairs=num_pairs)
# Parameters
params = {'batch_size': 1,
'shuffle': True,
'num_workers': 6}
# Datasets
# partition = {'train': pairs['male'], 'validation': data_subset[:10]} # IDs
# labels = {'id-1': 0, 'id-2': 1, 'id-3': 2, 'id-4': 1}
# Generators
training_set = Dataset(tr_pairs['males'], tr_pairs['females'])
training_generator = data.DataLoader(training_set, **params)
validation_set = Dataset(val_pairs['males'], val_pairs['females'])
validation_generator = data.DataLoader(validation_set, **params)
Train¶
def train(train_dataset, validation_dataset, epochs, device):
"""
X_m: Real male image from dataset
X_f: Real female image from dataset
y_m: Male label = 1
y_f: Female label = 0
"""
# Load model into GPU if available
model = cycleGAN().to(device)
for epoch in range(epochs):
print('Epoch', epoch+1, '------------------')
# Training
temp = 1
model.is_training = True
for X_m, X_f, y_m, y_f in train_dataset:
# Send input images to gpu if available.
X_m, X_f = X_m.to(device), X_f.to(device)
# Save loss values at the end of each epoch
if temp == train_dataset.__len__():
model.save_losses = True
model.optimize_parameters(X_m, X_f)
temp = temp+1
print('Tr - Total Generator Loss:', np.round(model.tr_gen_loss_dict['loss_gen_total'][-1], decimals=4))
print('Tr - Total Dicriminator Loss:', np.round(model.tr_dis_loss_dict['loss_dis_total'][-1], decimals=4))
model.save_losses = False
#if epoch % 10 == 0:
# Plot images each 10th epoch.
print_images(model.im_list, tr_im_save_dir, str(epoch), save_mode_on=True)
# Validation
with torch.set_grad_enabled(False):
temp = 1
model.is_training = False
for X_m, X_f, y_m, y_f in validation_dataset:
X_m, X_f = X_m.to(device), X_f.to(device)
if temp == validation_dataset.__len__():
model.save_losses = True
model.optimize_parameters(X_m, X_f)
temp = temp+1
print('----')
print('Val - Total Generator Loss:', np.round(model.val_gen_loss_dict['loss_gen_total'][-1], decimals=4))
print('Val - Total Dicriminator Loss:', np.round(model.val_dis_loss_dict['loss_dis_total'][-1], decimals=4))
model.save_losses = False
print_images(model.im_list, val_im_save_dir, str(epoch), save_mode_on=True)
# Save gen and disc loss values to respective csv files.
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(model.tr_gen_loss_dict)
df.to_csv(os.path.join(graph_save_dir, 'tr_gen_losses.csv'), index=False)
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(model.tr_dis_loss_dict)
df.to_csv(os.path.join(graph_save_dir, 'tr_dis_losses.csv'), index=False)
# Save gen and disc loss values to respective csv files.
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(model.val_gen_loss_dict)
df.to_csv(os.path.join(graph_save_dir, 'val_gen_losses.csv'), index=False)
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(model.val_dis_loss_dict)
df.to_csv(os.path.join(graph_save_dir, 'val_dis_losses.csv'), index=False)
# Save entire model architecture and params.
torch.save(model, os.path.join(model_save_dir, assign_model_id(model_save_dir)) + '.pth')
tr_im_save_dir, val_im_save_dir, graph_save_dir, model_save_dir = manage_folders()
print('\n-----Number of male/female image pairs-----\nTrain:', len(tr_pairs['males']))
print('Validation:', len(val_pairs['males']), '\n')
# Start training.
train(training_generator, validation_generator, epochs, device)
print('Finished.')
Some Output Examples on Validation Set¶
Below are some image translation examples performed on validation set during the training process. Notice the difference between the 1st and the other epochs. Model is obviously making progress by learning different sets of features from both domains, like long-hair of females and beards of males.
Structure of the output is as following:
- Real-A: Real image of a male
- Fake-B: Fake image of a female generated from a male image
- Recon-A: Reconstructed image of a male with a cycle generation to obtain the cycle loss (male->female->male)
- Identity-A: Male image generated by itself to obtain the identity loss.
The same structure is valid for the females when you simply swap the letters A and B.
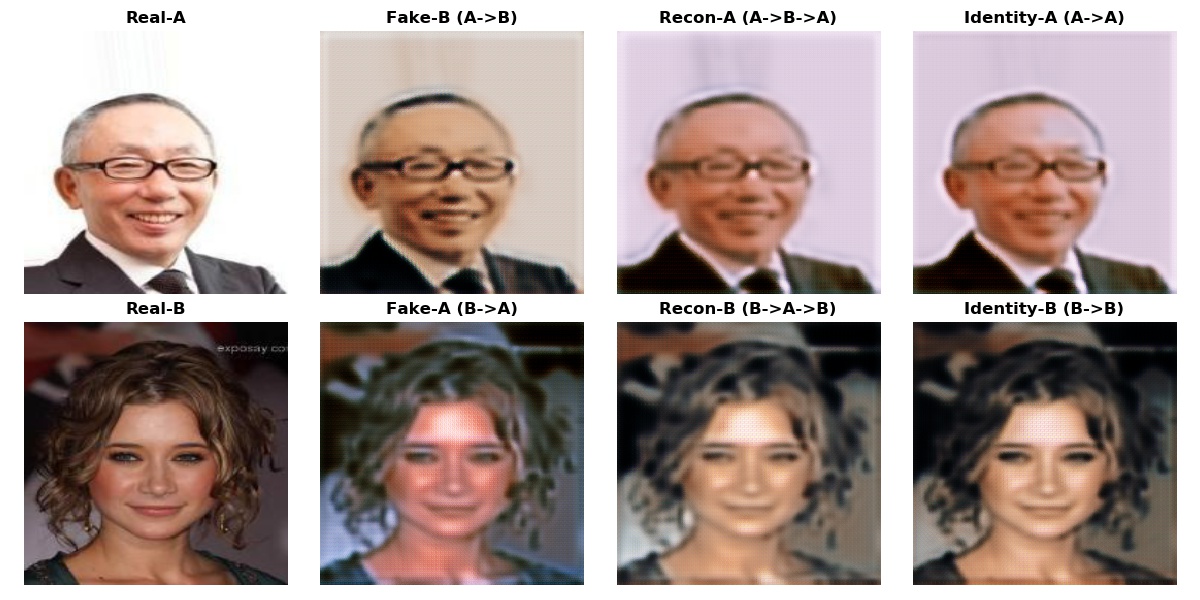
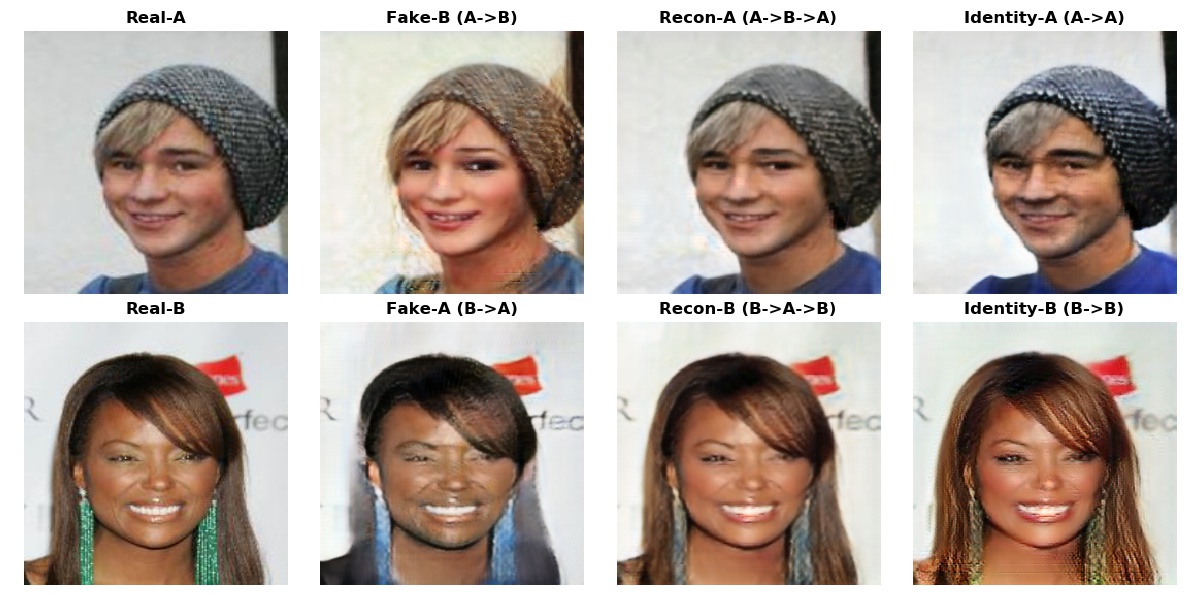
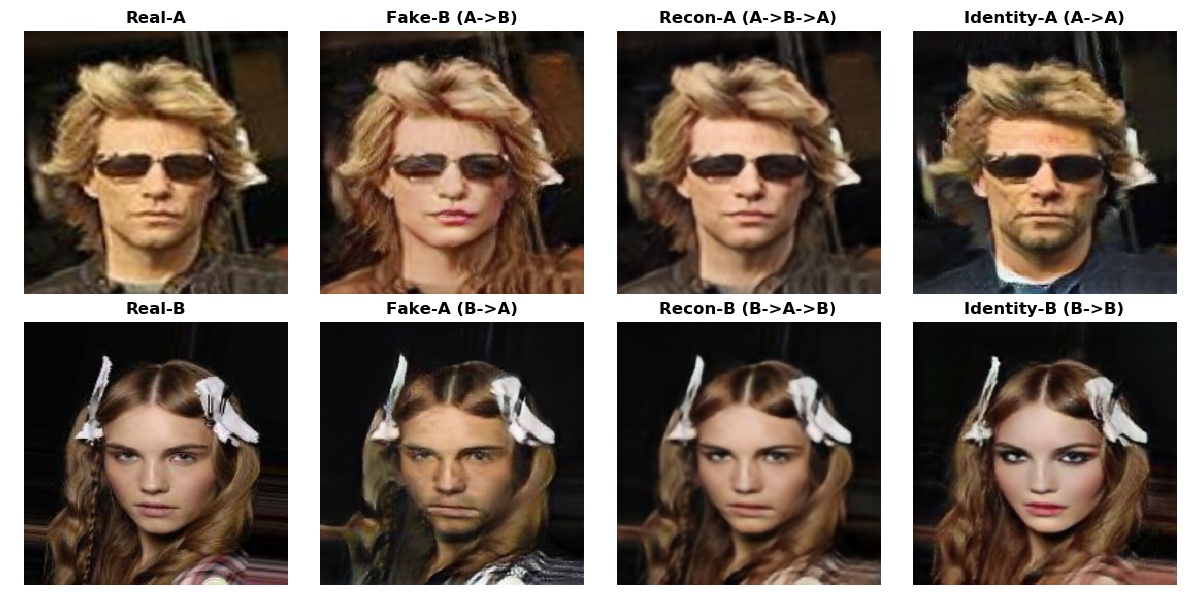



Note that the model tries to "erase" long hair from a female picture to swap it into a male, also adds on beard to the female pictures to do the vice-versa. Another interesting thing to observe is that the identity operation pretifies females by putting on some make up, while enhancing the masculin characteristics of the male pictures.